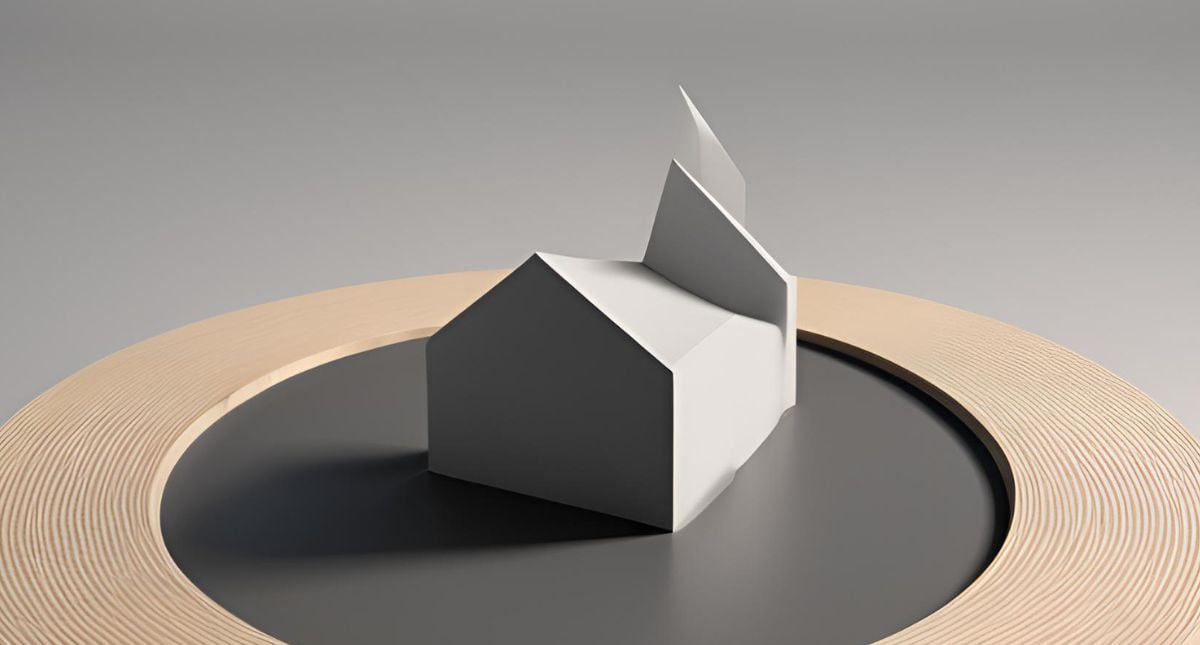


In today’s digitally-driven world, the field of computer-aided design (CAD) holds immense significance. As businesses across industries strive for innovation and efficiency, understanding the importance and function of CAD models becomes vital. This article delves into the world of CAD, demystifying the complexities and showcasing the practical applications that have revolutionized industries.
CAD models serve as the building blocks of design in various sectors, such as architecture, engineering, manufacturing, and more. These virtual representations enable designers to visualize, modify, and communicate their ideas with precision and accuracy. By transforming 2D designs into realistic 3D models, CAD software empowers professionals to explore virtually endless possibilities.
Furthermore, CAD models play a pivotal role in improving collaboration between different stakeholders throughout the design process. Architects can share their plans with contractors, engineers can analyze structural elements, and manufacturers can optimize production workflows. With the ability to detect design flaws and simulate real-world scenarios, CAD models ensure the final product meets the highest standards of quality and functionality.
Join us on a journey to discover the remarkable world of CAD, and learn how it enhances creativity, innovation, and problem-solving in diverse industries. Get ready to unlock the potential of virtual design and explore new horizons in the realm of computer-aided design.
CAD, or Computer-Aided Design, has revolutionized the way we conceptualize and bring ideas to life. At the heart of this transformative technology lies the fundamental role of models. These virtual representations serve as the building blocks for designers, engineers, and architects, enabling them to visualize, manipulate, and refine their creations before they are physically realized.
Models in CAD are digital renderings that capture the essential characteristics of a product, structure, or system. They provide a comprehensive and detailed view of the design, allowing professionals to explore various design iterations, analyze performance, and identify potential issues early in the development process. By working with these virtual models, designers can make informed decisions, optimize designs, and ensure the final product meets the desired specifications and requirements.
The versatility of CAD models extends beyond mere visualization. These digital representations serve as a common language, facilitating collaboration and communication among diverse stakeholders. Architects can share their building plans with construction teams, engineers can analyze structural components, and manufacturers can optimize production workflows. The ability to seamlessly exchange and interact with CAD models enables a more efficient and streamlined design and development process, ultimately leading to better-quality outcomes.
The adoption of CAD models in various industries has brought forth a wealth of benefits, revolutionizing the way design and engineering tasks are approached. One of the primary advantages of using CAD models is the enhanced accuracy and precision they offer. By creating detailed digital representations, designers can ensure that their ideas are captured with meticulous attention to detail, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies.
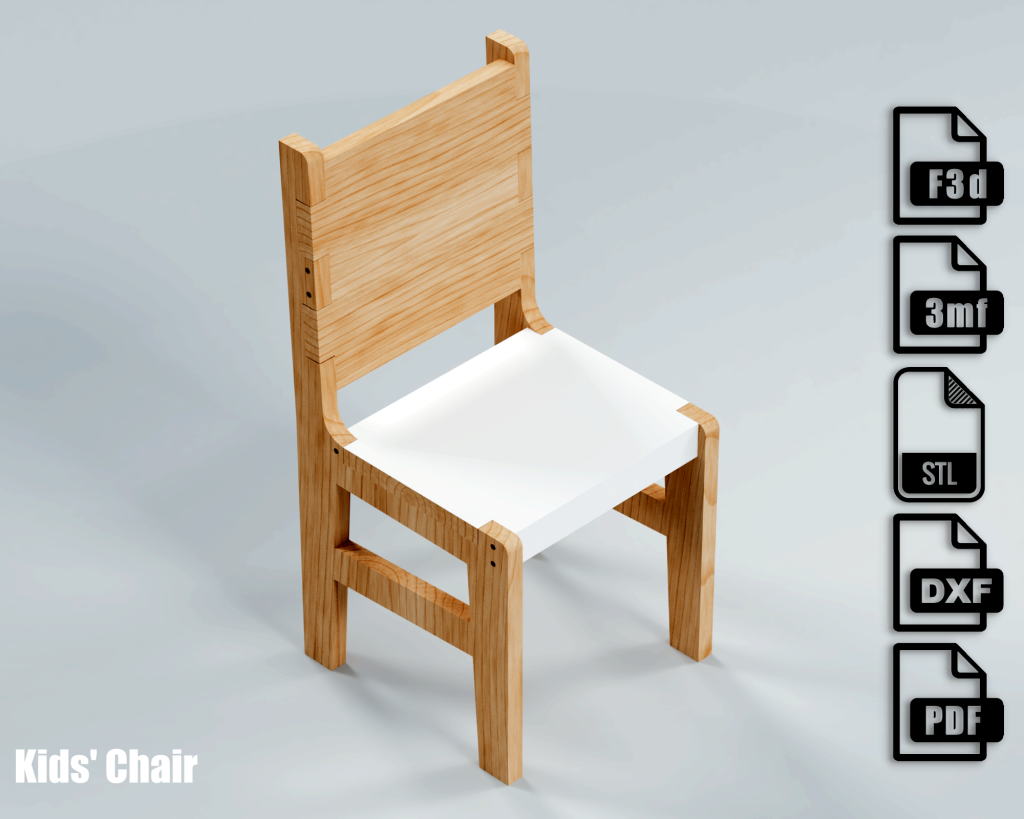

Child`s Chair 3d Editable Model, ready to be postprocessed and cut with a CNC Router.
Another significant benefit of CAD models is the ability to simulate and test design concepts virtually. Through the use of advanced simulation software, professionals can analyze the performance, behavior, and feasibility of their designs before investing in physical prototypes or production. This virtual testing allows for the identification and resolution of potential issues early in the design process, ultimately saving time, resources, and costs.
The flexibility and adaptability of CAD models are also noteworthy. As design requirements or specifications change, the digital models can be easily modified, manipulated, and updated to accommodate these changes. This agility enables designers to explore multiple design iterations, experiment with different materials or configurations, and make informed decisions without the constraints of physical limitations.
Furthermore, the integration of CAD models with other software systems, such as manufacturing and project management tools, enhances the overall efficiency of the design and production workflow. This seamless data exchange and integration streamline processes, reduce the risk of errors, and facilitate better collaboration among cross-functional teams.
In the expansive world of computer-aided design, there are several distinct types of CAD models, each serving a unique purpose and catering to specific industry needs. Understanding the different categories of CAD models is crucial for professionals to select the appropriate tools and techniques for their design projects.
One of the most common types of CAD models is the 3D model, which provides a comprehensive, three-dimensional representation of a product or structure. These models enable designers to visualize the object from various angles, explore its form, and analyze its spatial relationships. 3D CAD models are particularly valuable in industries such as architecture, engineering, and manufacturing, where the ability to create and manipulate complex geometries is essential.
Another prevalent type of CAD model is the 2D model, which captures the design in a two-dimensional format. These models are commonly used for technical drawings, schematics, and blueprints, providing a detailed representation of the object’s dimensions, specifications, and other critical information. 2D CAD models are widely employed in fields like construction, electrical engineering, and technical documentation.
Additionally, there are specialized types of CAD models, such as surface models and solid models. Surface models focus on the outer appearance and form of an object, while solid models represent the internal structure and volume of the design. These distinct model types cater to different design requirements and are often used in combination to achieve the desired level of detail and accuracy.
The world of CAD modeling is vast and diverse, encompassing a wide range of techniques and tools that enable designers, engineers, and architects to bring their ideas to life. From the fundamental wireframe models to the advanced parametric and feature-based modeling approaches, the CAD landscape offers a wealth of options to suit various design needs.
One of the foundational CAD modeling techniques is the wireframe model, which uses a series of lines and points to create a basic 3D representation of an object. This simplistic approach is often used as a starting point for more complex designs, allowing designers to establish the overall shape and structure of their creations.
Moving beyond the wireframe, the solid modeling technique emerged as a more sophisticated approach. Solid models represent the complete volume and internal structure of an object, providing a more realistic and detailed representation. This modeling method is particularly useful in industries such as manufacturing, where the accurate depiction of physical properties is crucial for product development and analysis.
Another prominent CAD modeling technique is the parametric modeling approach. This method allows designers to create models based on a set of predefined parameters, such as dimensions, materials, and constraints. By adjusting these parameters, designers can easily modify and iterate on their designs, making it an efficient and flexible tool for complex projects.
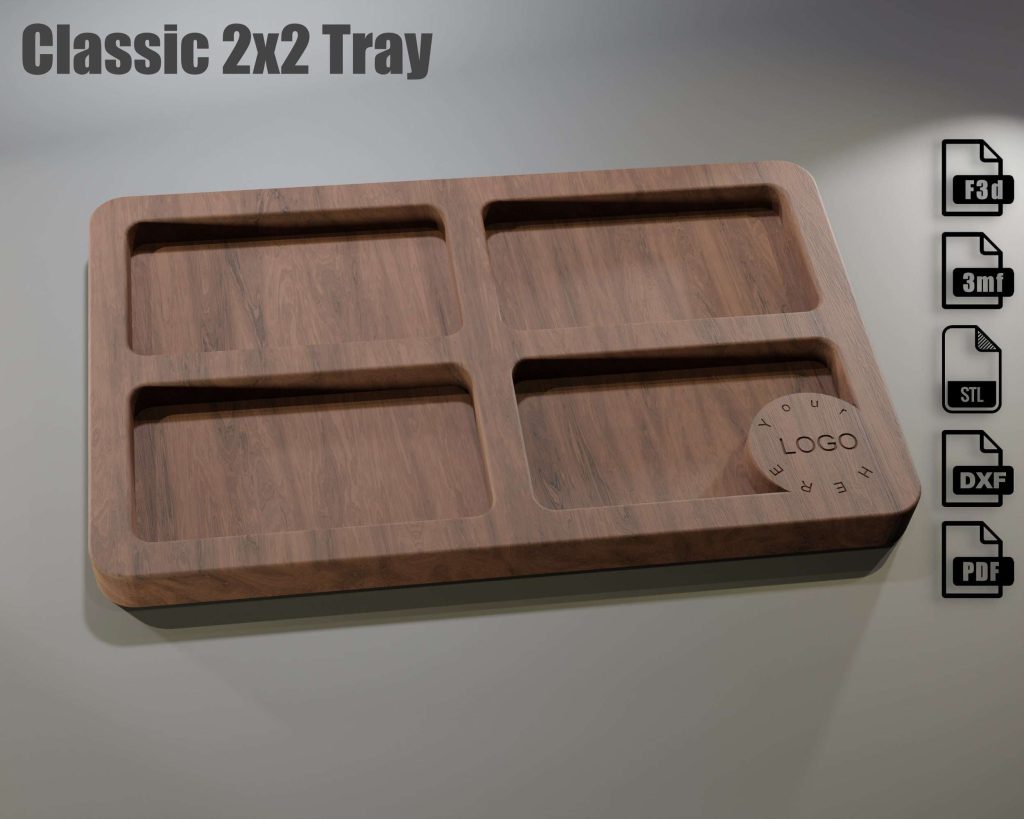

This is a digital file set for a classic 2×2 tray parametrically designed for CNC wood routers.
Includes: Fusion 360 editable parametric desing file, STL file (perfect for 3D printer imports), and DXF vector file (for laser cut profile). You will receive fully functional CNC digital design files along with your purchase.
We believe makers are people who make a difference in the world, and w…
Complementing these modeling techniques are the various CAD software tools available in the market. Industry-leading applications like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, and Autodesk Inventor offer a comprehensive suite of features and functionalities, empowering designers to create, manipulate, and analyze their CAD models with precision and efficiency. These tools often integrate seamlessly with other software systems, enabling a more streamlined and collaborative design workflow.
In the realm of computer-aided design, the importance of accurate and detailed CAD models cannot be overstated. These virtual representations serve as the foundation for the design, engineering, and manufacturing processes, and their level of precision and accuracy directly impacts the success of any project.
Accurate CAD models ensure that the final product or structure aligns precisely with the original design intent. By capturing every nuance and dimension of the design, these models enable designers and engineers to identify and address potential issues before they manifest in the physical world. This proactive approach not only enhances the overall quality of the end product but also saves time, resources, and costs associated with rework or retrofitting.
Moreover, detailed CAD models facilitate effective communication and collaboration among diverse stakeholders. When all parties involved in a project can visualize and interact with the same comprehensive digital representation, it fosters a shared understanding of the design, leading to better-informed decision-making and smoother project execution.
The level of detail in CAD models also plays a crucial role in the manufacturing and production processes. Highly detailed models provide the necessary information for computer numerical control (CNC) machines, 3D printers, and other fabrication tools to accurately produce the desired components or assemblies. This integration of CAD models with manufacturing processes ensures the seamless translation of digital designs into physical reality.
In industries such as architecture, engineering, and automotive, the accuracy and precision of CAD models are paramount. Structural integrity, aerodynamics, and ergonomics are all dependent on the fidelity of the digital representations. Inaccuracies or oversights in these models can lead to catastrophic consequences, underscoring the critical importance of meticulous attention to detail throughout the design and development stages.
The impact of CAD models extends far beyond the confines of a single industry, as they have revolutionized the way design and engineering tasks are approached across a diverse range of sectors. From architecture and construction to automotive and aerospace, the versatility of these virtual representations has transformed the way professionals conceptualize, visualize, and bring their ideas to life.
In the architectural and construction industries, CAD models have become an indispensable tool. Architects can create detailed 3D models of buildings, allowing them to visualize the structure, analyze its spatial relationships, and identify potential design flaws before the actual construction begins. These models also facilitate collaboration with engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders, ensuring seamless coordination and efficient project management.
The automotive industry has been a significant beneficiary of the advancements in CAD modeling. Car manufacturers rely on these virtual representations to design and engineer vehicles, optimizing everything from aerodynamics and structural integrity to ergonomics and aesthetics. CAD models enable engineers to simulate real-world scenarios, test various design iterations, and ensure the final product meets the highest standards of safety and performance.
In the aerospace sector, CAD models play a crucial role in the design and development of aircraft, spacecraft, and their components. These detailed digital representations allow engineers to analyze the behavior of complex systems, evaluate the impact of environmental factors, and optimize the overall performance of the final product. The integration of CAD models with advanced simulation software has revolutionized the way aerospace projects are conceived and executed.
The medical and healthcare industries have also embraced the power of CAD models, particularly in the realm of medical device design and development. Prosthetic limbs, surgical instruments, and implants can be meticulously designed and customized using CAD software, ensuring a perfect fit and optimal functionality for each patient. These virtual models also facilitate collaboration between medical professionals, engineers, and manufacturers, leading to more personalized and effective healthcare solutions.
While the advantages of CAD models are numerous and well-documented, the field of computer-aided design is not without its challenges. As the complexity of designs and the demands of various industries continue to evolve, CAD professionals must navigate a range of obstacles to ensure the seamless creation and implementation of these virtual representations.
One of the primary challenges in CAD modeling is the sheer volume and complexity of data involved. As designs become more intricate, the amount of information required to accurately capture and represent them increases exponentially. Managing and processing this vast amount of data can be a daunting task, often requiring specialized hardware, software, and expertise to ensure the models remain efficient and responsive.
Another significant challenge lies in the interoperability of CAD models across different software platforms and systems. Designers and engineers often use a variety of CAD tools, each with its own file formats and data structures. Ensuring the seamless exchange and integration of these models can be a complex and time-consuming endeavor, requiring the implementation of robust data exchange protocols and file conversion processes.
The need for continuous training and skill development is another challenge faced by CAD professionals. As the industry evolves and new technologies emerge, designers and engineers must constantly adapt and acquire new skills to stay relevant and maintain their proficiency in the field. This ongoing learning process can be both time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring a significant investment in professional development and education.
Additionally, the integration of CAD models with other software systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) and product lifecycle management (PLM) tools, can present unique challenges. Ensuring the smooth flow of information and the alignment of design data with broader business processes requires a deep understanding of system integration and data management principles.
Finally, the security and confidentiality of CAD models is a growing concern, particularly in industries where intellectual property and trade secrets are of utmost importance. Protecting these virtual representations from unauthorized access, modification, or distribution is a critical challenge that CAD professionals must address through the implementation of robust security measures and data governance protocols.
As the world of computer-aided design continues to evolve, the future holds exciting advancements and transformations that will shape the way designers, engineers, and professionals approach their work. By staying attuned to the emerging trends and technological innovations, we can gain insights into the direction of the CAD industry and the opportunities it presents.

One of the prominent trends in the future of CAD modeling is the increasing integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) technologies. These advanced computational capabilities can be leveraged to automate various aspects of the design process, from generative design and optimization to predictive analysis and decision-making. AI-powered CAD tools can assist designers in exploring a wider range of design alternatives, identifying optimal solutions, and streamlining the overall workflow.
The rise of cloud-based CAD platforms is another significant trend that is poised to transform the industry. By leveraging the power of cloud computing, designers and engineers can access their CAD models and collaborate on projects from anywhere, at any time. This cloud-based approach not only enhances the accessibility and flexibility of CAD tools but also enables seamless data sharing, version control, and remote team collaboration.
The integration of virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies with CAD modeling is another exciting development. These immersive technologies allow designers to experience their digital creations in a more intuitive and interactive manner, enabling them to better visualize and manipulate their designs. The ability to walk through virtual environments, interact with 3D models, and simulate real-world scenarios can significantly enhance the design process and improve the overall quality of the final product.
Furthermore, the advancements in additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, are expected to have a profound impact on the future of CAD modeling. As 3D printing technologies become more accessible and capable, designers can seamlessly transition from digital models to physical prototypes, accelerating the design-to-production cycle and enabling rapid iterations and customization.
Finally, the growing emphasis on sustainability and environmental considerations in design will shape the future of CAD modeling. Designers and engineers will need to incorporate eco-friendly materials, energy-efficient systems, and circular economy principles into their CAD models, ensuring that their designs are not only aesthetically pleasing and functionally sound but also environmentally responsible.
In the ever-evolving landscape of computer-aided design, the role of CAD models has become increasingly pivotal. These virtual representations serve as the foundation for innovation, collaboration, and problem-solving across a wide range of industries, from architecture and engineering to automotive and aerospace.
By understanding the importance and function of CAD models, professionals can harness the power of this transformative technology to enhance their design and development processes. The benefits of using CAD models, such as improved accuracy, enhanced collaboration, and the ability to simulate real-world scenarios, have revolutionized the way designers and engineers approach their work.
As the field of CAD continues to evolve, with the integration of emerging technologies like AI, cloud computing, and immersive VR/AR, the future holds even greater potential for the design and creation of innovative products, structures, and systems. By embracing these advancements and addressing the challenges that arise, CAD professionals can unlock new possibilities and drive progress in their respective industries.
Ultimately, the world of CAD modeling is a testament to the power of technology in shaping our built environment. By mastering the art of virtual design, we can unlock new frontiers of creativity, efficiency, and sustainability, paving the way for a future where innovation and problem-solving are limited only by our imagination.



Discover the World of CNC with Us! We're here to make your journey into CNC and making as smooth as possible. Whether you're a seasoned pro or just starting out, our goal is to provide you with fast navigation and clear guidance to help you find exactly what you're looking for. If you're new to the terminology, don't worry – we've got you covered! Check out our handpicked selection of products on Amazon, where you can find the perfect fit for your needs. And remember, when you make a purchase through our Amazon affiliate links, Agilemaking may receive commissions as compensation.
Happy exploring!
At AgileMaking.com, we focus on providing high-quality resources and content related to Computer Numerical Control (CNC). We strive to understand the needs of our community and offer customized solutions that drive excellence in digital manufacturing. We work collaboratively with our users to ensure long-term success in their CNC projects and operations.
Happy to have you here! Stay in the know with the latest trends, gain insights from our experts, and discover insider tips by making the AgileMaking Blog a regular stop. We’re genuinely excited to be your trusted resource as you explore the boundless possibilities of CNC and making. Welcome aboard, and enjoy the journey!